
Battle of the Bulge: A major push by the Germans during the final winter of WW2
When: December 1944
Where: Antwerp, Belgium
Why: To cut the British off from supplies and reinforcements.

V-1 or buzz bomb: The V1 flying bomb also known as the doodle bug, buzz bomb and V1 rocket, was a missile driven by a pulse jet engine
When: 1944
Where: Germany
Why: To be used by the Germans in World War 2 to bomb England, and get ready for the invasion of Britain.

V2 Rocket: Had a fully fuctional rocket engine, invented by the Germans, it was much faster than the V1. It also had a bigger warhead.
When: 1944
Where: Germany

Pearl Harbour: The Attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise Japanese assault on the U.S. Naval Base at Pearl Harbour.
When: December 7, 1944
Where: Pearl Harbour
Why: Pearl Harbor was a key American Naval Base in the Pacific, and the Japanese wanted to cripple the American Naval Standing in the Pacific.

Doolittle Raid: The Doolittle raid was the first American attack on the Japanese.
When: April 18 1942
Where: Honshu
Why: This was retaliation after the disaster at Pearl Harbour.

The Battle of the Coral Sea: This was one of the major turning points in the Pacific war. It was also the first battle where aircraft carriers engaged each other.
When: May 1942
Where: Pacific Ocean
Why: the Americans wanted to stop the Imperial Japanese Navy from moving south towards Australia.

The Battle of the Midway Islands: The battle was a pivotal point in World War 2 when the American and Japanese tension was reaching a very critical level.
When: Between 4 and 7 June 1942
Where: Midway Islands
Why: Another retaliation by the angry Americans.
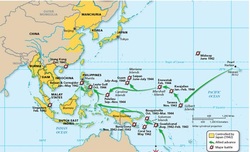
Island Hopping: Island hopping was a strategy used in the Pacific theater whereby selected islands were secured by allied forces.
When: N/A
Where: U.S.A to Japan.
Why: To shorten the trip to Japan.
Nationalism= Expressing the interests of one's own nation and viewing other nations inferior to yours.
Imperialism= The theory of acquiring foreign nations to be controlled under your nations rule.
Treaty of Versailles= The treaty put in place against Germany after World War 1 demanding Germany to pay Reparations.
Fourteen Points= A statement of the War aims.
Self- determination= Freedom of the people of a given area to determine their own political status.
War Guilt Clause= Germany had to accept that they were responsible for a damages against all other Allied powers.
W.C.T.U.= American organization, founded in November 1874 in Cleveland, Ohio, in response to the “Woman’s Crusade.
League of Nations= The Union that was formed to try and create a world police, it failed due to the USA not joining.
Collective Security= A system of maintaining world peace and security by concerted action on the part of the nations of the world.
Woodrow Wilson= 28th President of the United States, and formed the League of Nations.
Economic Sanctions= Actions taken by any nation(s) to harm the economy of another nation to force a political change.
Hoare-Laval Plan= Under this Pact, Italy would gain the best parts of Ogaden and Tigray, and economic influence over all the southern part of Abyssinia.
The Locarno Pact= A series of treaties, concluded in Locarno, Switzerland in 1925, between Germany, France, Belgium, the United Kingdom, Italy, Poland, and Czechoslovakia.
Kelogg- Briand Pact= The Kellogg-Briand Pact, also known as the Pact of Paris, was a treaty that attempted to outlaw war.
Washington Conference= The meeting between Roosevelt and Churchill between in May 1943, to plan Italian Campaign, air attacks on Germany and war in Pacific.
Bourgeoisie= The Middle Class
Proletariat= The class of industrial wage earners who, possessing neither capital nor production means, must earn their living by selling their labor.
Exploitation= Utilization of another person or group for selfish purposes.
Dictatorship= Absolute power by one ruler in Government.
Cadet= a student in training for service as a commissioned officer in the U.S. Army, Air force, or Coast Guard. Compare midshipman.
Bolshevik= A member of the more radical majority of the Social Democratic party, 1903–17, advocating immediate and forceful seizure of power by the proletariat.
Menshevik= a member of the Russian Social-Democratic Workers' party in opposition to the Bolsheviks.
October Manifesto= The October Manifesto was a document promising political reforms, issued by Tsar Nicholas II at the height of the 1905 Revolution.
Fundamental Laws= The law determining the constitution of the government of a state.
Duma= The Duma were council assemblies which were created by the Tsar of Russia.
Provisional Government= The Provisional Government is the name given to the government that led Russia from March 1917 to November 1917.
V.I. Lenin= Vladimir I. Lenin was a Russian communist and politician who served as Premier of the Soviet Union from 1922-1924.
Joseph Stalin=Joseph Stalin was the Premier of the Soviet Uniton from May 1941 until his death in March 1953. he was among the Bolshevik revolutionaries who brought about the Russian Revolution of 1917.
Leon Trotsky= Leon Trotsky was a Russian Marxist theorist and revolutionary known as the founder and leader of the Red Army as well as an important figure in the development of the Soviet Union.
Peace, Land, Bread= This was the battle cry of the 1917 October Revolution.
April Thesis= Lenin's April Theses form one of the most decisive manifestos in the history of the revolution.
Soviet= A person who is a supporter of the Soviet Union.
Alexander Kerensky= Alexander Kerensky was a major political leader preceding and during the Russian Revolutions of 1917. He served as the second Prime Minister of the Russian Provisional Government before Vladimir Lenin was elected following the October Revolution.
General Kornilov= Being a major general he was a high value prisoner of war, but in July 1916 Kornilov managed to escape back to Russia and return to duty.
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk= A separate peace treaty that the Soviet government was forced to sign on March 3, 1918 after almost six-month-long negotiations.
War Communism= War communism or military communism was the economic and political system that existed in Soviet Russia.
The Russian Civil War= The Russian Civil War (7 November (25 October) 1917 – October 1922) was a multi-party war in the former Russian Empire fought between the Bolshevik Red Army and the White Army, the loosely allied anti-Bolshevik forces.
Reds/Whites= The Red Army defeated the White Armed Forces.
Allied Intervention= The Allied intervention was a multi-national military expedition launched during the Russian Civil War in 1918.
New Economic Policy= The New Economic Policy (NEP) was introduced to replace the failed policy of War Communism.
Comintern= The name given to the Third International, founded at Moscow in 1919.
Treaty of Rapallo= An agreement signed at the Hotel Imperiale in the Italian town of Rapallo on 16 April, 1922 between Germany and Russia.
“Guns or Butter”= A classic model of the production possibility curve by using the relationship between "guns", or military spending, and "butter", or food supplies.
Command Economy= An economy where supply and price are regulated by the government rather than market forces.
Collectivization= Collectivization in the Soviet Union was enforced under Stalin between 1928 and 1940.
Kolkhoz= A form of collective farms in the Soviet Union. Kolkhoz existed along with state farms or sovkhoz.
Kulak= Kulaks were a category of relatively affluent farmers in the later Russian Empire, Soviet Russia, and early Soviet Union.
Five Year Plan= Soviet economic practice of planning to augment agricultural and industrial output by designated quotas for a limited period of time
Gulags= The Gulag was the Soviet Union government agency that administered the main Soviet forced labor camp systems during the Stalin era.
The Purges= The purges in the USSR allowed Stalin to get rid of supposed enemies who he believed threatened him.
Gustav Stresemann= Gustav Stresemann was a German politician and statesman who served as Chancellor in 1923.
Intro
The Port Theatre, is a non for profit theatre in the coastal city of Nanaimo, British Columbia. It was opened in 1998 after beginning construction in 1989. Since then the theatre has been host to a wide range of shows including live theatre, concerts, and film festivals.
Tourism
(https://www.google.ca/search?q=nanaimo+port+theatre&tbm=bks&tbo=1) Located in the Downtown core of Nanaimo,the theatre is located across from the Nanaimo Harbour, and a ten minute drive from the BC Ferries, Departure Bay Terminal. Because of this central location many busses (http://www.transitbc.com/regions/nan/schedules/2012.03.04.images/nan_map_nanaimo.pdf) run by the facility allowing for ease of access from most places in Nanaimo.
Facilities
The Port Theatre is home to two Main areas, the Main Stage, and the Harmac Pacific Room.
Main Stage This Stage and seating Area.This area makes up the majority of the theatre, with 604 seats on the main level and another 200 on the balcony coming to a total of 804 seats. The stage includes a sprung stage floor able to hold hundreds of tons worth of scenery, without injuring dancers.
Harmac Pacific Room This room is a small business area on the second floor designed for use by 35 people or less.
Features
804 seats in total (604 on the main level and 200 in the balcony)
28 seating areas accessible without stairs
Excellent viewing from all seats
Maple panels and cement walls enhance acoustics. The first two rows of seats sit on the orchestra lift. With the push of a button the lift goes down, the seats are removed and there is room for up to 34 musicians in the orchestra pit. We can also put the lift at the stage level which creates a thrust stage out into the audience
chamber.The sprung stage floor is built to withstand many tons of rolling scenery and yet is soft enough for dancers not to hurt themselves while jumping.
The theatre has 48 line-sets for stage draperies, lights and scenery. The deep stage allows lots of room for performers and sets. Stage proscenium arch is adjustable: from 42 to 48 feet wide. Minimum of 12 computerized pieces of equipment to operate lighting & audio systems.
References
http://www.porttheatre.com/theatre-info/history-mandate http://www.transitbc.com/regions/nan/schedules/map.cfm?region=0 http://www.porttheatre.com/ link to port theatre home page
http://www.porttheatre.com/theatre-info/seating-chart









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed